
If the corporation behaves recklessly or fraudulently, then shareholders without separation can be held liable as well—and their personal assets, how is sales tax calculated such as their homes, are at risk of being seized. C-corp shareholders are generally not liable for the corporation’s debts or obligations. Instead, liability is limited to their financial interest in the corporation, and third parties looking to satisfy debts must look to the corporation itself.

Pros and Cons of C Corporations
- When a C Corp distributes assets to a shareholder, the corporation also pays tax on any gain in value of that asset.
- A C corporation is a type of company owned by shareholders who elect a board of directors to manage the company’s operations.
- Because a C corporation is a legal entity distinct from its owners, it can enter into contracts and is liable for its debts.
- The shareholders are required to report the amount they received on their personal income tax returns, and pay taxes on it.
- This person keeps records of all company-related matters and actions.
The current corporate income tax rate is a flat 21%, following the removal of a tiered system with the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. For comparison, the current maximum personal income tax rate is 37% for incomes above roughly a half million dollars. In essence, an S-corp combines the tax privileges of a partnership with the corporate protections of a C-corp. The word “corporation” may be thrown around casually as a synonym for a big business, but there’s quite a bit more to it than that.
- A C corporation (or C corp) is a legal structure for a corporation in which the owners, or shareholders, are taxed separately from the entity.
- Let’s say that Diego and Chloe want to go into business together.
- As part of that, we recommend products and services for their success.
- You should check the governing statute and the bylaws to see the percentage vote required.
- A C corporation can have an unlimited number of shareholders and can issue any type of stock (common or preferred).
Types of Corporations
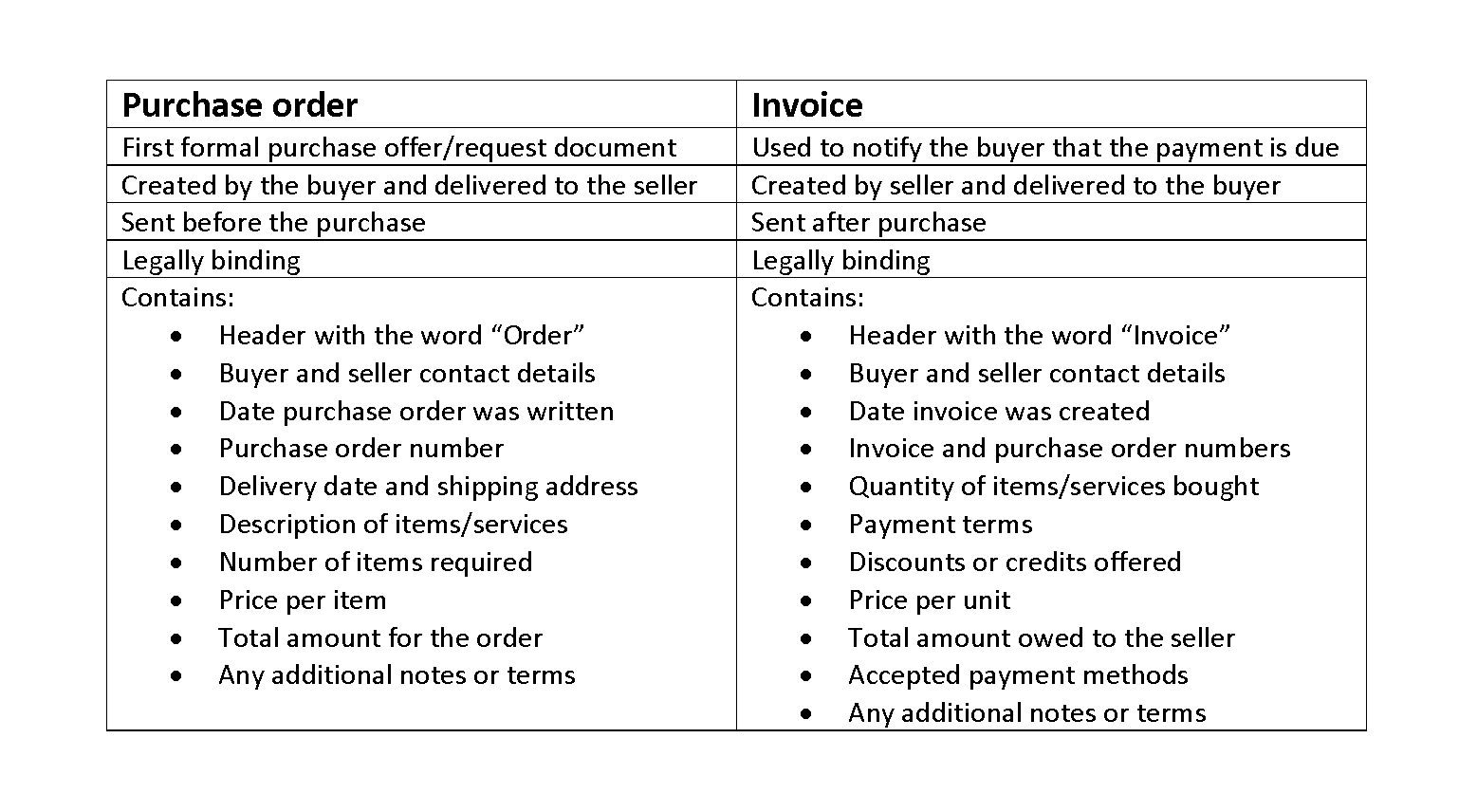
Filing of annual reports, financial disclosure reports, and financial statements is mandatory under law. One of the requirements of C corporation status is to hold at least one shareholders and directors meeting annually. Minutes must be recorded to exhibit transparency in business operations.

C Corporation Advantages & Disadvantages
There is no one best option among the possible business or tax structures. The choice should be based on the specific situation of each business, and business owners should consult with legal and tax professionals during the process. Plenty of businesses that begin as partnerships and LLCs eventually transition to C-corp status. Regardless of what you plan for your business, it’s important to have a clear understanding of each option so you can weigh pros and c corp meaning cons carefully.
How much of a difference does it make to pay corporate income taxes vs. personal income taxes?
C corporations file IRS Form 1120 to report corporate income taxes. Additionally, they may have to manage other liabilities such as Social Security and Medicare taxes, depending on employee count and business structure. Keep an eye on proposed tax changes, like the Biden Administration’s recent push to raise the corporate tax rate from 21% to 28%. The C corp entity itself is subject to corporate income taxation, while shareholders are subject to personal taxation. In simple terms, a C corp pays tax on its income just as an individual would pay tax on their yearly salary—a law firm chart of accounts flat 21% on operational profits.

